| WW2 and History Collection / Weapons and
Equipment / Ships / Country U / United States / USS Langley
(CV 1 / AV 3) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Updated: |
May 21st, 2016 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
United States of
America |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| USS
Langley (CV 1 / AV 3) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
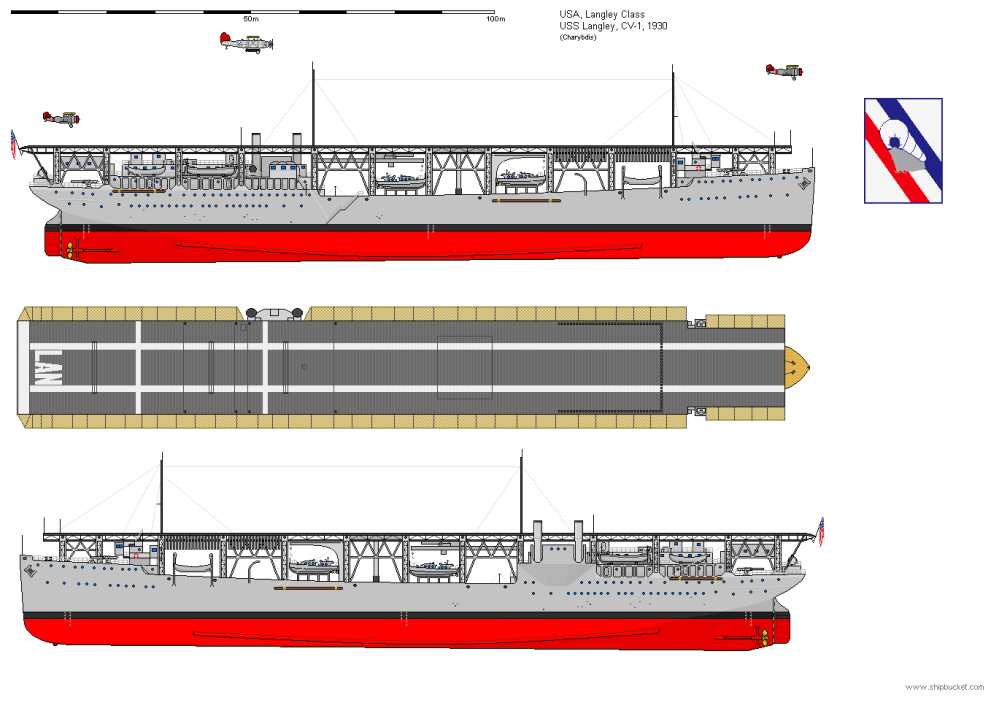
| The USS Langley was the
first Aircraft Carrier of the US Navy and was obtained by converting
the fleet collier USS
Jupiter
(AC 3). The ship was converted to Seaplane Tender with the same
name
but the pennant number AV 3. On February 27th, 1942 the ship was bombed
by Japanese aircraft. The burning hull was sunk by her escortships USS
Whipple (DD 217) and USS Edsall (DD 219) on February 28th, 1942 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
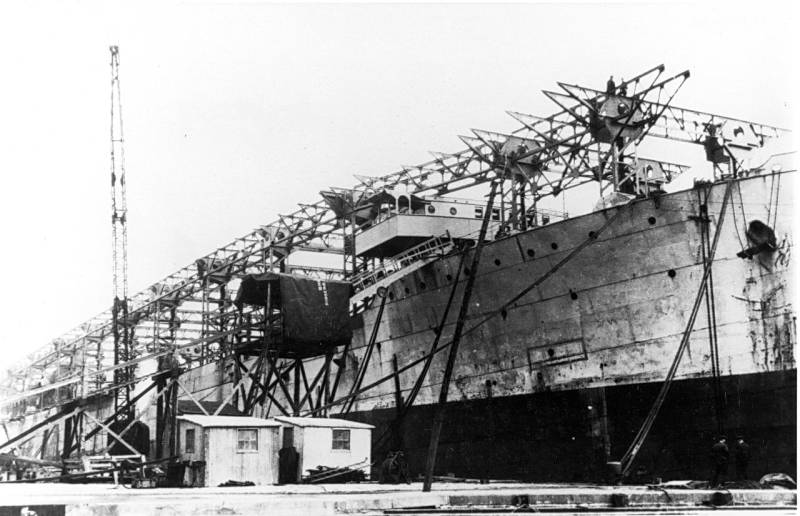
| USS Jupiter under conversion to USS
Langley |
USS Langley and USS Somers (DD 301) near San Diego, 1928 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History On July 11th, 1919, USS Jupiter was designated to become an aircraft carrier and left for Hampton Roads, Virginia on December 12th, 1919. Here the ship was decommissiones on March 24th, 1920. The conversion took place at the Navy Yard in Norfolk, Virginia. She was renamed to USS Langley on April 11th, 1920, in honor for Samuel Pierpont Langley, an American astronomer, physicist, aeronautics pioneer and aircraft engineer. On March 20th, 1922, the ship was recommissioned as USS Langley (CV 1). The first plane to be launched from her flightdeck was a Vought VE-7, piloted by Lieutenant Virgil C. Griffin on October 17th, 1922. The first decklanding was performed on October 26th, 1922 when Lieutenant Commander Godfrey de Courcelles Chevalier landed his Aeromarine 39B on the ship. Commander Kenneth Whiting made the first catapult start on November 18th, 1922. One special feature in the ships design was the carrier pigeon house on the stern of the ship. Since the First World War, seaplanes used to carry pigeons to send over messages. Trained at the Norfolk Shipyard, the pigeons were used for training purposes on board the ship. At sea it was no problem to make the pigeons return to the ship, but when USS Langley anchored near Norfolk shipyard, the pigeons tend to fly off to the cranes of the shipyard, for there they were trained. Although also on board the USS Lexington (CV 2) and USS Saratoga (CV 3) the pigeons were planned, the navy did not use them anymore. On USS Langley the pigeon house was transformed to the quarters of the Executioner Officer. After initial training, USS Langley started flight operations in the Caribbean on January 15th, 1923. The ship cruised the Atlantic coast and the Caribbean until late 1924, when she transferred to the Pacific Battle Fleet on November 29th, 1924. In 1927 the ship was stationed at Guantanamo Bay Naval Base and later operated along the Californian Coast and Hawaii. In 1929 she participated in the film "The Flying Fleet". USS Langley sailed into Mare Island Navy Yard, California on October 25th, 1936, to be converted to a seaplane tender. Her conversion was completed on February 26th, 1937. USS Langley was assigend to the Aircraft Scouting Force and received the hull classification number AV 3 on April 11th, 1937. Between February 1st, 1939 and July 10th, 1939, the ship was assigned to the Atlantic Fleet. September 24th, 1939 she returned to the Pacific Fleet. When Japanese forces attacked hte Philippines on December 8th, 1941, USS Langley was anchored at Cavite. Evading the Japanese forces, she departed for Balikpapan, Dutch East Indies and later for Darwin, Australia, where the ship arrived on January 1st, 1942. Here the ship was assigned to American-British-Dutch-Australian Command (ABDACOM), performing anti-submarine patrols near Darwin until January 11th, 1942. The ship then departed for Fremantle to join ms Sea Witch. wjere both ships loaded crates with 32 Curtiss P-40 fighters from 13th Pursuit Squadron (Provisional), Far East Air Force. On February 22nd, 1942, USS Langley and ms Sea Witch departed in Convoy MS 5, together with USAT Willard A. Holbrook (AP 44), mv Duntroon and ss Katoomba, escorted by USS Phoenix (CL 46). On February 27th, 1942, USS Langley and ms Sea Witch left the convoy and met up with escorts USS Whipple (DD 217) and USS Edsall (DD 219). At 11.40 hrs, the ships sailed at 121 km south of Tjilatjap, when Mitsubishi G4M Betty bombers attacked them. During the third sweep, USS langley was hit by five bombs, killing 16 of her crewmembers. The upper structure burned and the ship soon listed 10 degrees to her portside. At 13.32 hrs, the order was given to abandon ship. The escorts tried to finish the ship off with nine 100 mm shells and two torpedoes to prevent the ship falling in enemy hands. When the escorts left, the ship was still not sunken, but is supposed to have sunk later at approximately 8.51'S - 109.02'E. Most survivors were picked up by the escorts and some were later transferred to the USS Pecos (AO 6). Many of them later were killed when both USS Pecos and USS Edsall also were sunk by Japanese planes. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
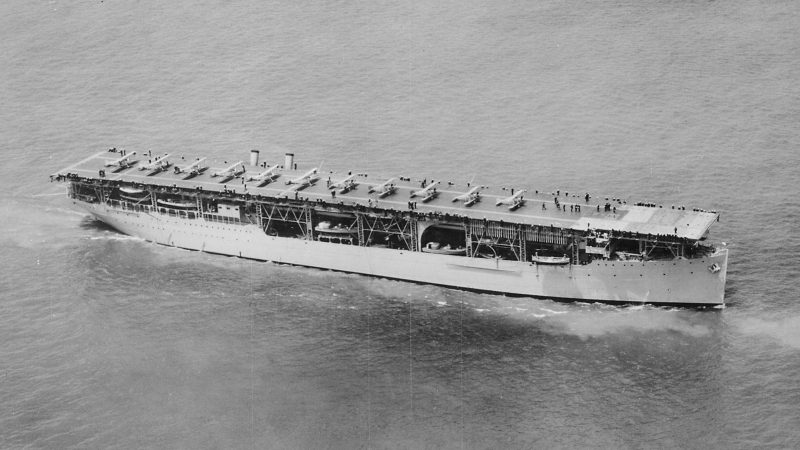
| USS Langley (CV 1) | USS Langley, Culebra Island, Puerto
Rico, March 18th, 1926 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| For her service USS Langley was awarded the: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
American Defence Service Streamer, with "FLEET" clasp. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
Asiatic Pacific Campaign Streamer | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
World War Two Victory Streamer | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
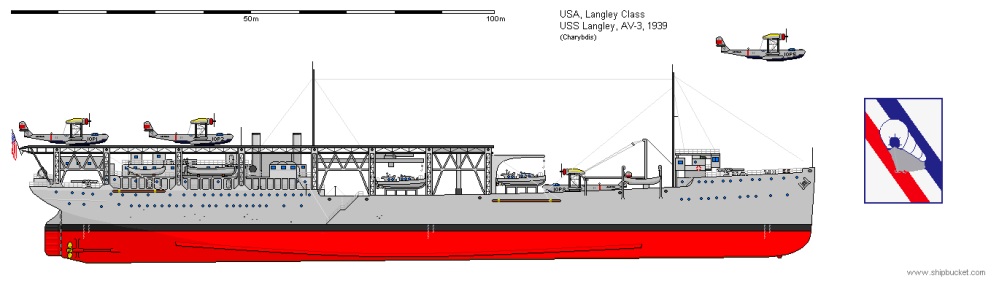
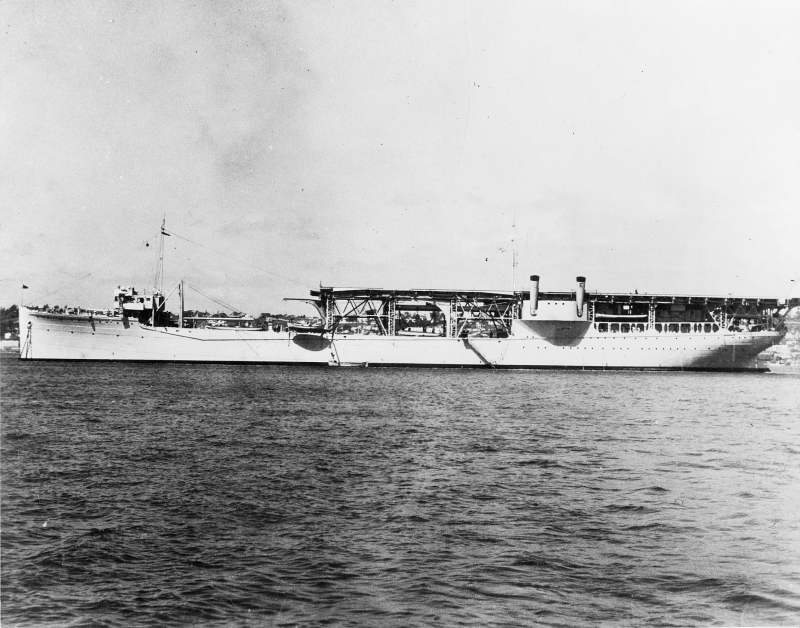
| USS Langley (AV 3), 1937 | USS Langley, French Frigate Shoals, 1937 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
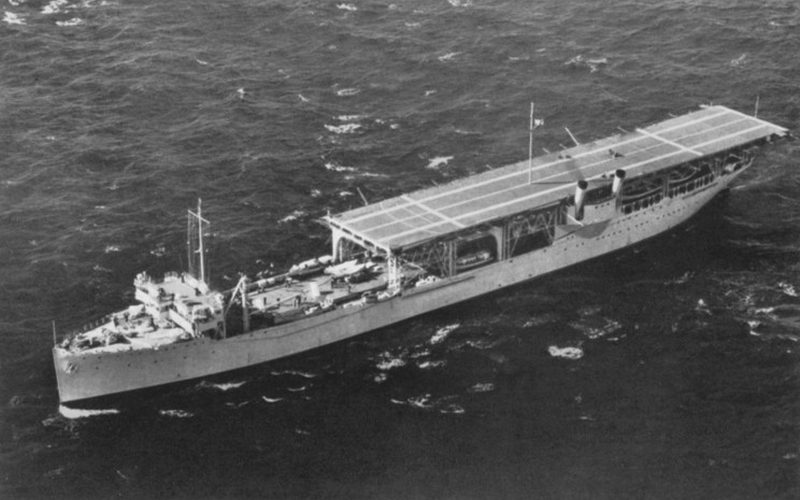
| Topvieuw of USS Langley |
USS Langley, Darwin, February 19th, 1942 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
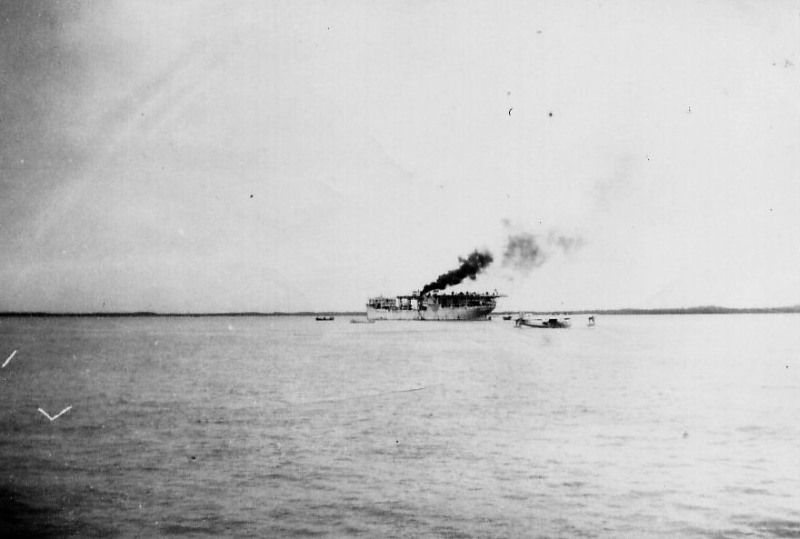
| The sinking USS Langley, February 27th, 1942 | The crippled USS Langley, being abandoned by her crew, taken on board by USS Edsall (DD 219), seen from USS Whipple (DD 217) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
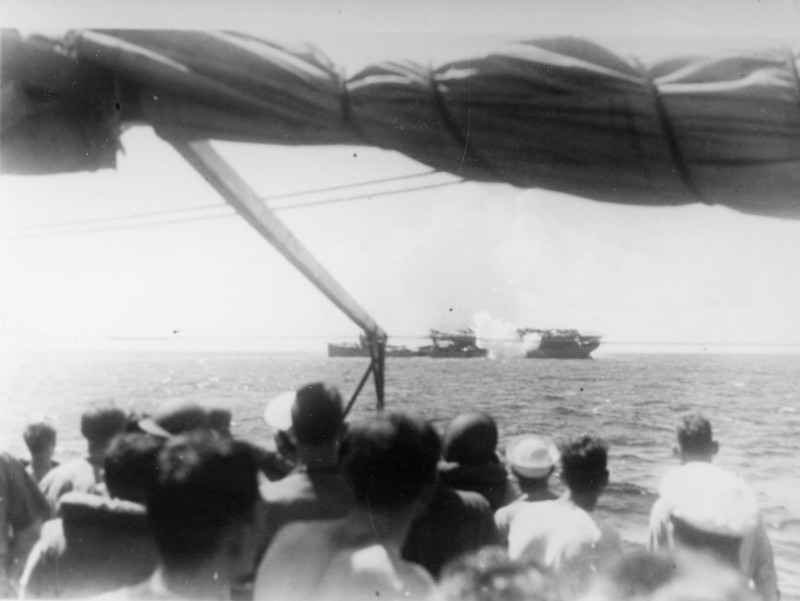
| USS Langley (AV 3) at the moment a torpedo from USS Whipple (DD 217) explodes, February 27th, 1942 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Text:
Wilco Vermeer Sources: - USS Langley/Wikipedia (Retrieved, January 30th, 2015) - Naval History and Heritage Command (Retrieved January 30th, 2015) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| © WW2 History Collection, Wilco Vermeer, 2014 - 2016 |
contact | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||











